Sessions 22 to 23|Java Exception Handling¶
- Java Exception Handling by Durga Sir
- Exception Handling in Java
What is an Exception?¶
- An exception is an event that occurs during the execution of a program.
- It disrupts the normal flow of the program.
- When an exception occurs, an Exception Object is created, which contains information about the error, such as:
- The type of exception and its message.
- The stack trace, etc.
- The runtime system uses this Exception Object to locate the class or block of code that can handle the exception.
In [1]:
public class Main {
void method1() {
method2();
}
void method2() {
method3();
}
void method3() {
int value = 50/0;
}
}
Main main = new Main();
main.method1();
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero at Main.method3(#12:11) at Main.method2(#12:7) at Main.method1(#12:3) at .(#14:1)
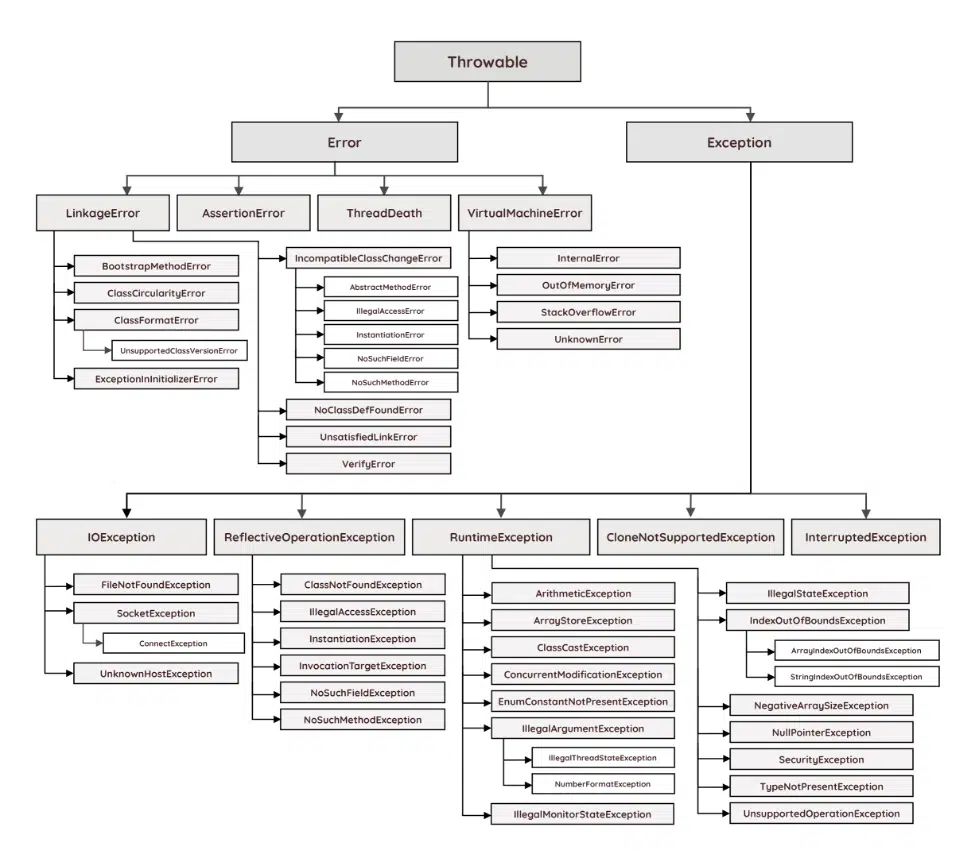
Exception Hierarchy¶
- Object
- Throwable
- Error
StackOverflowErrorOutOfMemoryError
- Exception
- Unchecked/Runtime Exceptions
ClassCastExceptionArithmeticExceptionIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionStringIndexOutOfBoundsException
NullPointerExceptionIllegalArgumentExceptionNumberFormatException
- Checked/Compile-time Exceptions
ClassNotFoundExceptionInterruptedExceptionIOExceptionFileNotFoundExceptionEOFExceptionSocketException
SQLException
- Unchecked/Runtime Exceptions
- Error
- Throwable
Runtime Exceptions¶
These exceptions occur during runtime, and the compiler does not force us to handle them.
In [2]:
public class Main {
public void method1() {
throw new ArithmeticException("Division by Zero");
}
}
Main main = new Main();
main.method1();
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- java.lang.ArithmeticException: Division by Zero at Main.method1(#12:3) at .(#15:1)
In [3]:
Object val = 0;
System.out.println((String)val);
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- java.lang.ClassCastException: class java.lang.Integer cannot be cast to class java.lang.String (java.lang.Integer and java.lang.String are in module java.base of loader 'bootstrap') at .(#17:1)
In [4]:
int[] val = new int[2];
val[3];
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 3 out of bounds for length 2 at .(#18:1)
In [5]:
String val = null;
val.charAt(0);
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- java.lang.NullPointerException: Cannot invoke "String.charAt(int)" because "REPL.$JShell$16C.val" is null at .(#19:1)
In [6]:
Integer.parseInt("abc");
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "abc" at java.base/java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:67) at java.base/java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:662) at java.base/java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:778) at .(#20:1)
Compile-time Exceptions¶
These exceptions are checked by the compiler during code compilation. If they are not handled properly, the code will fail to compile.
In [7]:
public class Main {
public void method1() {
throw new ClassNotFoundException();
}
}
Main main = new Main();
main.method1();
| throw new ClassNotFoundException(); unreported exception java.lang.ClassNotFoundException; must be caught or declared to be thrown
Handling Exceptions Using "throws"¶
In [8]:
public class Main {
public void method2() {
method1();
}
public void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException {
throw new ClassNotFoundException();
}
}
Main main = new Main();
main.method1();
| method1(); unreported exception java.lang.ClassNotFoundException; must be caught or declared to be thrown
Handling Exceptions Using "try/catch"¶
- The
tryblock specifies the code that may throw an exception. - The
tryblock is followed by either acatchblock, afinallyblock, or both. - The
catchblock is used to handle exceptions thrown within thetryblock. - Multiple
catchblocks can be used to handle different types of exceptions.
In [9]:
public class Main {
public void method2() {
try {
method1();
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException exception) {
System.out.println(exception.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("Hello");
}
public void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException {
throw new ClassNotFoundException("Class Not Found");
}
}
Main main = new Main();
main.method2();
Class Not Found Hello
In [10]:
public class Main2 {
public void method2() {
method1();
}
public void method1() {
try {
throw new ClassNotFoundException("Class Not Found");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException exception) {
System.out.println(exception.getMessage());
}
}
}
Main2 main = new Main2();
main.method2();
Class Not Found
Catch Multiple Exceptions in a Single Block¶
In [11]:
public class Main {
public void method2() {
try {
method1("boom");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException | InterruptedException exception) {
System.out.println(exception.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("Hello");
}
public void method1(String str) throws ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
if (str.equals("dummy")) {
throw new ClassNotFoundException("Class Not Found");
} else {
throw new InterruptedException("Interrupted Exception Occurred");
}
}
}
Main main = new Main();
main.method2();
Interrupted Exception Occurred Hello
Catch all Exception Object¶
In [12]:
public class Main3 {
public void method2() {
try {
method1();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException exception) {
System.out.println(exception.getMessage());
} catch (Exception exception) {
System.out.println(exception.getMessage());
}
}
public void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException, FileNotFoundException {
throw new FileNotFoundException("FileNotFound Exception Occurred");
}
}
Main3 main = new Main3();
main.method2();
FileNotFound Exception Occurred
In [13]:
public class Main3 {
public void method2() {
try {
method1();
} catch (Exception exception) { // it should be the last catch block
System.out.println(exception.getMessage());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException exception) {
System.out.println(exception.getMessage());
}
}
public void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException, FileNotFoundException {
throw new FileNotFoundException("FileNotFound Exception Occurred");
}
}
Main3 main = new Main3();
main.method2();
| } catch (ClassNotFoundException exception) { | System.out.println(exception.getMessage()); | } exception java.lang.ClassNotFoundException has already been caught
Try/Catch/Finally or Try/Finally Block¶
- The
finallyblock can be used after thetryblock or after thecatchblock. - The
finallyblock is always executed, whether you return from thetryblock or thecatchblock. Only onefinallyblock can be added. - It is mostly used for tasks like closing resources, logging, etc.
- If JVM-related issues occur, such as out-of-memory errors, system shutdowns, or the process being forcefully terminated, the
finallyblock may not be executed.
In [14]:
public class Main {
public void method2() {
try {
method1("boom");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | InterruptedException exception) {
System.out.println(exception.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}
public void method1(String str) throws ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
if (str.equals("dummy")) {
throw new ClassNotFoundException("Class Not Found");
} else {
throw new InterruptedException("Interrupted Exception Occurred");
}
}
}
Main main = new Main();
main.method2();
Interrupted Exception Occurred Hello World
Why Do We Need Exception Handling?¶
- It helps keep the code clean by separating error-handling code from the regular code.
- It allows the program to recover from errors.
- It enables us to add more information, which aids in debugging.
- It improves security by hiding sensitive information.
Custom Exception¶
In [15]:
public class CustomException extends RuntimeException {
CustomException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
In [16]:
public class Main {
public void method2() {
method1();
}
public void method1() throws CustomException {
throw new CustomException("Hello");
}
}
Main main = new Main();
main.method2();
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- REPL.$JShell$28$CustomException: Hello at Main.method1(#12:7) at Main.method2(#12:3) at .(#29:1)